Contents

Bloody tissue emerging from a belly button piercing can raise alarms, indicating potential complications that demand attention. Despite the popularity of these piercings, issues like trauma, allergic reactions, or infections can arise, disrupting the healing process. Understanding the complexities of these challenges is crucial for ensuring a safe and successful piercing experience.
Belly button piercings have surged in popularity as a fashionable form of body modification, adorning the midriff with unique and decorative jewelry. However, amidst the allure of these piercings, there’s a less glamorous side that can emerge – the presence of bloody tissue.
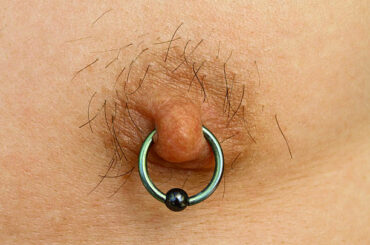
Bloody tissue coming out of a belly button piercing can be alarming and is often indicative of underlying issues. Despite its unsettling nature, this phenomenon is not uncommon and warrants attention to ensure proper healing and avoid complications.
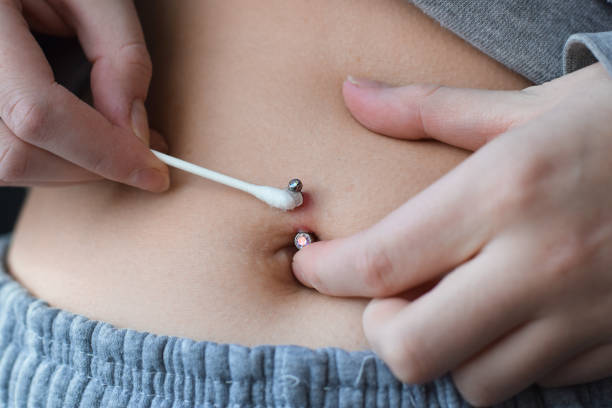
The procedure for getting a belly button piercing typically involves the insertion of a hollow needle through the navel’s skin and underlying tissue, followed by the placement of a jewelry piece. While this process is generally straightforward, it does puncture the skin, creating a wound that requires diligent care to prevent infection and promote healing.
However, sometimes the healing process doesn’t go as smoothly as planned. Bloody tissue may emerge from the piercing site, signaling various potential complications. This could include trauma to the piercing site, an allergic reaction to the jewelry material, or, most concerning, an infection.
Infections are a primary concern when dealing with bloody tissue from a belly button piercing. The warm, moist environment around the navel provides an ideal breeding ground for bacteria, which can easily enter the wound during the piercing process or through improper aftercare practices. If left untreated, an infection can escalate, leading to more severe symptoms such as increased pain, swelling, and pus discharge.
It’s essential for individuals experiencing bloody tissue from their belly button piercings to promptly address the issue. Ignoring the problem or attempting to self-diagnose and treat it can exacerbate the situation, potentially leading to further complications and prolonged healing times.
In the following sections, we will delve deeper into the potential causes of bloody tissue from belly button piercings, explore preventive measures to minimize the risk of complications, and provide guidance on when to seek professional medical attention. Understanding the factors contributing to this issue and taking proactive steps can help ensure a safe and successful piercing experience.

Bloody tissue around a belly button piercing can be a distressing sight and may indicate several underlying factors contributing to its development. Understanding these potential causes is crucial for effective management and prevention of complications.
1. Improper Piercing Technique: When a belly button piercing is performed incorrectly, it can lead to trauma to the surrounding tissue, resulting in bleeding and the formation of bloody tissue. This might occur if the piercer uses unsterilized equipment, employs incorrect piercing methods, or fails to consider the individual’s anatomy, leading to undue pressure or damage to the area.
2. Poor Aftercare Practices: Inadequate or improper aftercare can exacerbate the risk of bloody tissue around a belly button piercing. Neglecting to clean the piercing site regularly with a saline solution or using harsh cleaning agents can irritate the delicate skin, potentially causing inflammation, bleeding, and delayed healing. Consistent and gentle care is essential for facilitating proper healing and minimizing complications.
3. Allergic Reactions: Some individuals may experience allergic reactions to the materials used in their belly button jewelry, such as nickel or certain metals. These allergic reactions can manifest as redness, itching, swelling, and, in severe cases, the presence of bloody tissue around the piercing site. Choosing hypoallergenic jewelry options and avoiding known allergens can help prevent this issue.
4. Infections: Bloody tissue around a belly button piercing may also indicate the presence of an infection, which is a serious concern requiring prompt attention. Infections can occur due to bacterial, viral, or fungal pathogens entering the wound during or after the piercing procedure. Factors such as poor hygiene practices, exposure to contaminated water, or touching the piercing with unclean hands can increase the risk of infection. Symptoms may include increased pain, swelling, warmth, discharge, and the formation of pus.
5. Trauma or Injury: Accidental trauma or injury to the piercing site can lead to bleeding and the formation of bloody tissue. Activities such as wearing tight clothing, participating in contact sports, or snagging the jewelry on objects can cause tissue damage and disrupt the healing process. Additionally, rough handling during cleaning or changing of jewelry can exacerbate the problem, leading to bleeding and irritation.
6. Underlying Health Conditions: Certain underlying health conditions, such as diabetes, autoimmune disorders, or circulatory problems, can impact the body’s ability to heal properly and increase the risk of complications with piercings. Individuals with compromised immune systems or impaired wound healing may be more susceptible to infections, delayed healing, and the development of bloody tissue around the piercing site.
Addressing the underlying cause of bloody tissue around a belly button piercing is essential for promoting healing and preventing further complications. By identifying contributing factors such as improper piercing technique, poor aftercare practices, allergic reactions, or underlying health conditions, individuals can take proactive steps to resolve the issue and ensure a successful piercing experience.

When bloody tissue emerges around a belly button piercing, it’s essential to address the issue promptly to prevent further complications and promote proper healing. Treatment options may vary depending on the underlying cause and severity of the problem, but several approaches can be effective in resolving the issue.
1. Proper Wound Care: The foundation of treatment for bloody tissue around a belly button piercing involves maintaining proper wound care practices. This includes gently cleaning the piercing site with a saline solution or mild soap and water twice daily to remove debris, reduce inflammation, and prevent infection. Avoiding harsh cleaning agents or excessive manipulation of the piercing can help minimize further irritation and promote healing.
2. Topical Treatments: In cases where infection is suspected or confirmed, topical treatments such as antibiotic ointments or antiseptic solutions may be recommended to help combat bacterial growth and promote wound healing. Applying these treatments directly to the piercing site can help reduce inflammation, alleviate discomfort, and prevent the spread of infection to surrounding tissues.
3. Oral Antibiotics: If the bloody tissue is accompanied by signs of infection, such as pus discharge, increasing pain, or fever, oral antibiotics may be prescribed to address the underlying bacterial infection. These medications work systemically to eliminate harmful bacteria from the body and reduce the risk of complications. It’s essential to complete the full course of antibiotics as prescribed by a healthcare professional to ensure effective treatment.
4. Piercing Removal: In severe cases where the piercing site fails to heal properly despite appropriate treatment measures or if complications such as persistent infection or piercing rejection occur, removal of the piercing may be necessary. Removing the jewelry allows the wound to close naturally and reduces the risk of further complications. However, piercing removal should only be performed by a trained professional to minimize the risk of additional trauma or damage to the surrounding tissue.
5. Consultation with a Healthcare Professional: If bloody tissue persists despite efforts to manage it at home or if there are concerns about the severity of the issue, seeking guidance from a healthcare professional is advisable. A doctor or dermatologist can assess the piercing site, provide a definitive diagnosis, and recommend appropriate treatment options based on individual needs and circumstances. They can also offer advice on preventive measures to reduce the risk of future complications with piercings.
It’s crucial to monitor the piercing site closely throughout the treatment process and seek medical attention if there are any signs of worsening symptoms or complications. With proper care and timely intervention, bloody tissue around a belly button piercing can be effectively managed, allowing for successful healing and a positive piercing experience.
4. Prevention Tips to Avoid Bloody Tissue Around Belly Button Piercings
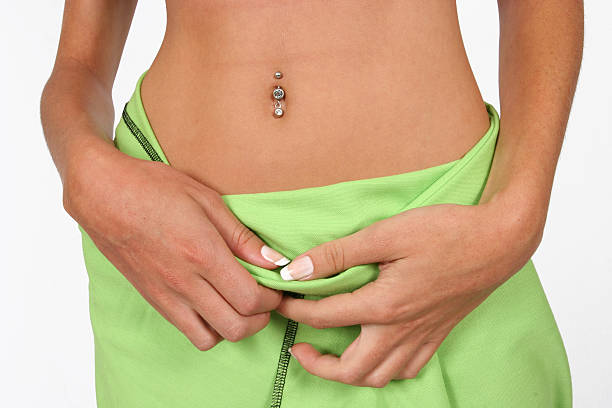

Preventing complications with belly button piercings is key to minimizing the risk of encountering issues such as the emergence of bloody tissue. By following these practical tips and guidelines, individuals can promote proper healing and reduce the likelihood of complications:
1. Follow Aftercare Instructions: Adhering to proper aftercare instructions provided by the piercer is essential for supporting the healing process and preventing infections or irritation that can lead to bloody tissue. This includes cleaning the piercing site regularly with a saline solution or mild soap and water, as well as avoiding touching or twisting the jewelry unnecessarily.
2. Avoid Harsh Chemicals or Irritants: When caring for a belly button piercing, it’s important to steer clear of harsh cleaning agents, alcohol-based solutions, or other irritants that can disrupt the delicate balance of the skin and increase the risk of inflammation or bleeding. Stick to gentle, non-abrasive cleansers and avoid applying excessive force when cleaning the piercing site.
3. Choose Hypoallergenic Jewelry: Opting for hypoallergenic jewelry made from high-quality materials such as surgical-grade stainless steel, titanium, or niobium can help minimize the risk of allergic reactions that may result in inflammation, itching, or the formation of bloody tissue. Avoid jewelry containing nickel or other common allergens, especially if you have a history of sensitivity to certain metals.
4. Practice Good Hygiene: Maintaining good hygiene practices is essential for preventing infections and promoting healing after getting a belly button piercing. Wash your hands thoroughly with soap and water before touching the piercing site, and avoid swimming in pools, hot tubs, or natural bodies of water until the piercing has fully healed to reduce the risk of exposure to bacteria or contaminants.
5. Monitor for Signs of Infection: Stay vigilant for signs of infection, such as increased pain, swelling, redness, warmth, or the presence of pus or bloody discharge around the piercing site. If you notice any concerning symptoms, promptly seek advice from a healthcare professional to prevent the infection from worsening and potentially leading to more severe complications.
6. Avoid Trauma or Injury: Be mindful of activities that may put undue stress or strain on the piercing, such as wearing tight clothing, engaging in contact sports, or participating in activities that involve direct pressure or impact on the navel area. Take care when changing clothes or engaging in physical activities to avoid accidentally snagging or tugging on the jewelry, which can cause trauma and lead to bleeding.
By following these prevention tips and prioritizing proper care and attention to your belly button piercing, you can minimize the risk of complications and promote a smooth healing process. Remember to be proactive in addressing any concerns or symptoms, including the presence of bloody tissue, and seek guidance from a professional if needed to ensure a positive piercing experience.
Conclusion
In conclusion, belly button piercings have undoubtedly become a popular form of self-expression, adding a touch of personal style to the midriff. However, alongside the allure of these piercings, there exists a less glamorous aspect that cannot be ignored – the potential presence of bloody tissue.
Bloody tissue around a belly button piercing can be alarming and often signals underlying issues such as infection, trauma, allergic reactions, or poor aftercare practices. Addressing the underlying cause of bloody tissue is essential for promoting healing and preventing further complications.
Throughout this article, we’ve explored various aspects related to belly button piercings, from their introduction and typical procedure to potential causes of complications and available treatment options. We’ve emphasized the importance of proper aftercare, attentive monitoring for signs of infection, and seeking professional guidance when needed to ensure a safe and successful piercing experience.
By following preventive measures such as proper wound care, avoiding harsh chemicals or irritants, choosing hypoallergenic jewelry, practicing good hygiene, and being mindful of signs of infection, individuals can minimize the risk of encountering issues like bloody tissue around their belly button piercings. Taking proactive steps and prioritizing proper care and attention can ultimately contribute to a smoother healing process and a more enjoyable piercing experience.
Remember, if you experience any concerns or symptoms, including the presence of bloody tissue, don’t hesitate to seek guidance from a healthcare professional or your piercer. Your health and well-being are paramount, and by staying informed and proactive, you can navigate the journey of body piercing with confidence and peace of mind.